waa.h File Reference
WAA functions header file. More...
#include <ctype.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "global.h"
#include "actions.h"

Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | waa__entry_blocks_t |
| Entry list for disk-order update. More... | |
Defines | |
| #define | max(a, b) |
| Max macro. | |
| #define | WAA__MAX_EXT_LENGTH |
| #define | FCB__PUT_DOTSLASH (1) |
| #define | FCB__NO_REALPATH (2) |
| #define | HEADER_LEN (64) |
| How many bytes the dir file header has. | |
| #define | WAA_VERSION (6) |
| Which version does the dir file have? | |
| #define | SET_REVNUM (-12) |
| Copy URL revision number. | |
Per working copy | |
| #define | WAA__DIR_EXT "dir" |
| #define | WAA__IGNORE_EXT "Ign" |
| #define | WAA__URLLIST_EXT "urls" |
| #define | WAA__COPYFROM_EXT "Copy" |
Per file/directory | |
| #define | WAA__FILE_MD5s_EXT "md5s" |
| #define | WAA__PROP_EXT "prop" |
| #define | WAA__CONFLICT_EXT "cflct" |
Temporary copy/move detection database | |
| #define | WAA__FILE_INODE_EXT "fino" |
| For files. | |
| #define | WAA__DIR_INODE_EXT "dino" |
| For directories. | |
Temporary copy/move detection database | |
| #define | WAA__FILE_NAME_EXT "fname" |
| For files. | |
| #define | WAA__DIR_NAME_EXT "dname" |
| For directories. | |
Short names for the open modes. | |
| #define | WAA__WRITE (O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC) |
| #define | WAA__READ (O_RDONLY) |
| #define | WAA__APPEND (O_APPEND | O_CREAT) |
Functions | |
| int | waa__save_cwd (char **where, int *len, int additional) |
| Store the current working directory. | |
| int | waa__init (void) |
| Initialize WAA operations. | |
| int | waa__mkdir_mask (char *dir, int including_last, int mask) |
Create a directory; ignore EEXIST. | |
| int | waa__mkdir (char *dir, int including_last) |
Create a directory, ignore EEXIST, and use a default mask. | |
| int | waa__open (char *path, const char *extension, int mode, int *filehandle) |
| Base function to open files in the WAA. | |
| int | waa__close (int filehandle, int has_failed) |
This function closes a writable filehandle that was opened in the WAA via waa__open(). | |
| int | waa__open_dir (char *directory, int write, int *fh) |
| Wrapper function. | |
| int | waa__build_tree (struct estat *root) |
Creates the entries tree below root . | |
| int | waa__output_tree (struct estat *root) |
Write the dir file for this root . | |
| int | waa__input_tree (struct estat *root, struct waa__entry_blocks_t **blocks, action_t *callback) |
| Read the dir file for the current working directory. | |
| int | waa__open_byext (char *directory, char *extension, int write, int *fh) |
Wrapper function for waa__open(). | |
| int | waa__load_repos_urls (char *dir, int reserve_space) |
Wrapper for waa__load_repos_urls_silent(). | |
| int | waa__load_repos_urls_silent (char *dir, int reserve_space) |
Load the URLs associated with dir (or current working directory, if dir is NULL). | |
| int | waa__given_or_current_wd (char *directory, char **erg) |
Returns the given directory or, if NULL , getcwd() . | |
| int | waa__make_info_link (char *directory, char *name, char *dest) |
| Creates a symlink in the WAA. | |
| int | waa__delete_byext (char *path, char *extension, int ignore_not_exist) |
| This function takes a path and an extension and tries to remove the associated file in the WAA. | |
| int | waa__read_or_build_tree (struct estat *root, int argc, char *normalized[], char *orig[], action_t *callback, int return_ENOENT) |
| Reads the entry tree or, if none stored, builds one. | |
| int | waa__find_common_base2 (int argc, char *args[], char ***normalized_paths, int flags) |
| Given a list of path arguments the base path and relative paths are returned. | |
| static int | waa__find_common_base (int argc, char *args[], char **normalized[]) |
| Wrapper for waa__find_common_base2. | |
| int | waa__find_base (struct estat *root, int *argc, char ***args) |
| Similar to waa__find_common_base(), but allows only specification of a WC root. | |
| int | waa__create_working_copy (const char const *wc_dir) |
| Creates the WAA and CONF directories needed for wc_path. | |
| int | waa__set_working_copy (const char const *wc_dir) |
| Stores the path of the working copy. | |
| int | waa__update_tree (struct estat *root, struct waa__entry_blocks_t *blocks) |
This function traverses the tree and sets entry_status for the marked entries. | |
| int | waa__new_entry_block (struct estat *entry, int count, struct waa__entry_blocks_t *previous) |
| Insert an entry block with count entries into the waa__entry_blocks list, to get it updated later by waa__update_tree(). | |
| static int | waa__insert_entry_block (struct estat *entry, int count) |
| Simple wrapper; inserts entries at the start of the list. | |
| int | waa__partial_update (struct estat *root, int argc, char *normalized[], char *orig[], struct waa__entry_blocks_t *blocks) |
| The given paths are looked for in the entries tree, are marked for update, and their parents are flagged. | |
| int | waa__do_sorted_tree (struct estat *root, action_t handler) |
| This function traverses the tree and calls the handler function for the marked entries; directories before their children, and in order sorted by name. | |
| int | waa__dir_enum (struct estat *this, int est_count, int by_name) |
A wrapper around dir__enumerator(), ignoring entries below $FSVS_WAA. | |
| int | waa__copy_entries (struct estat *src, struct estat *dest) |
| Copies all sub-entries of src to dest. | |
| int | waa__get_tmp_name (const char *base_dir, char **output, apr_file_t **handle, apr_pool_t *pool) |
| Returns a distict name and filehandle. | |
Variables | |
| struct waa__entry_blocks_t | waa__entry_block |
| First block for to-be-updated pointers. | |
| char * | wc_path |
| Our current WC base. | |
| int | wc_path_len |
| How much bytes the wc_path has. | |
| int | waa_tmp_path_len |
| Length of paths of temporary files. | |
| char * | waa_tmp_path |
| Buffers for temporary filename storage. | |
| char * | waa_tmp_fn |
| char * | conf_tmp_path |
| char * | conf_tmp_fn |
Building paths for FSVS's datafiles. | |
| #define | GWD_WAA (1) |
| The path should be in the WAA. | |
| #define | GWD_CONF (2) |
| The path should be in the configuration area. | |
| #define | GWD_MKDIR (4) |
| The intermediate directories should be created. | |
| int | waa__get_waa_directory (char *path, char **erg, char **eos, char **start_of_spec, int flags) |
| This function determines the directory used in the WAA area for the given path. | |
| static int | waa__get_gwd_flag (const char *const extension) |
| Function that returns the right flag for the wanted file. | |
Detailed Description
WAA functions header file.
Definition in file waa.h.
Define Documentation
| #define FCB__NO_REALPATH (2) |
| #define FCB__PUT_DOTSLASH (1) |
| #define GWD_CONF (2) |
The path should be in the configuration area.
Definition at line 289 of file waa.h.
Referenced by ign___load_group(), st__print_entry_info(), waa__create_working_copy(), waa__find_common_base2(), waa__get_gwd_flag(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__make_info_link().
| #define GWD_MKDIR (4) |
The intermediate directories should be created.
Definition at line 291 of file waa.h.
Referenced by hsh___new_bare(), waa__create_working_copy(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__make_info_link().
| #define GWD_WAA (1) |
The path should be in the WAA.
Definition at line 287 of file waa.h.
Referenced by st__print_entry_info(), waa__create_working_copy(), waa__get_gwd_flag(), and waa__get_waa_directory().
| #define HEADER_LEN (64) |
How many bytes the dir file header has.
Definition at line 341 of file waa.h.
Referenced by ign__save_ignorelist(), waa__input_tree(), and waa__output_tree().
| #define max | ( | a, | |||
| b | ) |
Value:
({ typeof (a) _a = (a); \
typeof (b) _b = (b); \
_a > _b ? _a : _b; })
Taken from gcc info manual. >? and <? are only for C++.
Definition at line 25 of file waa.h.
Referenced by waa__init().
| #define SET_REVNUM (-12) |
Copy URL revision number.
The problem on commit is that we send a number of entries to the repository, and only afterwards we get to know which revision number they got. To avoid having to run through the whole tree again we use this special marker, which gets set on the committed entries, to be corrected on ops__save_1entry().
Definition at line 352 of file waa.h.
Referenced by cs__set_file_committed(), and ops__save_1entry().
| #define WAA__MAX_EXT_LENGTH |
Value:
max( \ max( \ max(strlen(WAA__CONFLICT_EXT), \ strlen(WAA__COPYFROM_EXT)), \ strlen(WAA__IGNORE_EXT) ), \ max( \ max(max(strlen(WAA__DIR_EXT), \ strlen(WAA__FILE_MD5s_EXT)), \ max(strlen(WAA__PROP_EXT), \ strlen(WAA__CONFLICT_EXT)) ), \ max( \ max(strlen(WAA__FILE_INODE_EXT), \ strlen(WAA__DIR_INODE_EXT)), \ max(strlen(WAA__FILE_NAME_EXT), \ strlen(WAA__DIR_NAME_EXT)) ) ) )
Definition at line 186 of file waa.h.
Referenced by waa__init().
| #define WAA_VERSION (6) |
Which version does the dir file have?
Definition at line 343 of file waa.h.
Referenced by waa__input_tree(), and waa__output_tree().
Function Documentation
| int waa__build_tree | ( | struct estat * | dir | ) |
Creates the entries tree below root .
Creates the entries tree below root .
All entries are defined as new.
Definition at line 939 of file waa.c.
References ac__dispatch, approx_entry_count, estat::by_inode, DEBUGP, estat::entry_count, estat::entry_status, FS_NEW, ign__is_ignore(), sstat_t::mode, estat::name, ops__are_children_interesting(), ops__free_marked(), ops__mark_changed_parentcc, ops__set_todo_bits(), estat::st, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, estat::to_be_ignored, waa__build_tree(), and waa__dir_enum().
Referenced by bld__work(), waa__build_tree(), and waa__update_dir().

| int waa__close | ( | int | filehandle, | |
| int | has_failed | |||
| ) |
This function closes a writable filehandle that was opened in the WAA via waa__open().
This function closes a writable filehandle that was opened in the WAA via waa__open().
If has_failed is !=0, the writing to the file has failed somewhere; so the temporary file is not renamed to the destination name, just removed.
This may be called only for writeable files of waa__open() and similar; readonly files should just be close()d.
Definition at line 712 of file waa.c.
References DEBUGP, waa___temp_names_t::dest_name, IF_FREE, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, waa___temp_names_t::temp_name, and waa__mkdir().
Referenced by cs___mnbs_close(), ign__save_ignorelist(), res__mark_conflict(), res__remove_aux_files(), url__output_list(), and waa__output_tree().

Copies all sub-entries of src to dest.
Copies all sub-entries of src to dest.
dest must already exist; its name is not overwritten, as it is (usually) different for the copy base entry.
Existing entries of dest are not replaced or deleted; other entries are appended, with a status of FS_REMOVED.
This works for both directory and non-directory entries.
Definition at line 2839 of file waa.c.
References estat::by_name, estat::entry_count, hlp__calloc(), IF_FREE, sstat_t::mode, estat::name, ops__allocate(), ops__copy_single_entry(), ops__correlate_dirs(), ops__new_entries(), estat::parent, estat::st, STOPIF, and waa__copy_entries().
Referenced by cm___make_copy(), and waa__copy_entries().

| int waa__create_working_copy | ( | const char const * | wc_dir | ) |
Creates the WAA and CONF directories needed for wc_path.
Creates the WAA and CONF directories needed for wc_path.
The dir must be absolute; this function makes an own copy, so the value will be unchanged.
Definition at line 3004 of file waa.c.
References BUG_ON, GWD_CONF, GWD_MKDIR, GWD_WAA, STOPIF, waa__get_waa_directory(), waa__make_info_link(), waa__mkdir(), waa__set_working_copy(), and wc_path.
Referenced by co__work(), and url__work().

| int waa__delete_byext | ( | char * | path, | |
| char * | extension, | |||
| int | ignore_not_exist | |||
| ) |
This function takes a path and an extension and tries to remove the associated file in the WAA.
This function takes a path and an extension and tries to remove the associated file in the WAA.
If the unlink()-call succeeds, the (max. 2) directory levels above are removed, if possible.
Via the parameter ignore_not_exist the caller can say whether a ENOENT should be returned silently.
If extension is NULL, the given path already specifies a file, and is not converted into a WAA path.
- See also:
- Files used by fsvs.
Definition at line 836 of file waa.c.
References BUG_ON, DEBUGP, PATH_SEPARATOR, STOPIF, waa__get_gwd_flag(), and waa__get_waa_directory().
Referenced by hsh__close(), ign__save_ignorelist(), res__remove_aux_files(), rev__install_file(), sync__progress(), sync__work(), and up__unlink().
| int waa__dir_enum | ( | struct estat * | this, | |
| int | est_count, | |||
| int | by_name | |||
| ) |
A wrapper around dir__enumerator(), ignoring entries below $FSVS_WAA.
A wrapper around dir__enumerator(), ignoring entries below $FSVS_WAA.
The cwd is the directory to be looked at.
IIRC the inode numbers may change on NFS; but having the WAA on NFS isn't a good idea, anyway.
Definition at line 2803 of file waa.c.
References DEBUGP, sstat_t::dev, dir__enumerator(), hlp__lstat(), sstat_t::ino, STOPIF, and waa_stat.
Referenced by waa__build_tree(), and waa__update_dir().

This function traverses the tree and calls the handler function for the marked entries; directories before their children, and in order sorted by name.
Definition at line 2773 of file waa.c.
References estat::by_name, dir__sortbyname(), estat::do_this_entry, IF_FREE, estat::parent, STOPIF, waa___recurse_tree(), and waa__do_sorted_tree().
Referenced by st__work(), and waa__do_sorted_tree().

| int waa__find_base | ( | struct estat * | root, | |
| int * | argc, | |||
| char *** | args | |||
| ) |
Similar to waa__find_common_base(), but allows only specification of a WC root.
Definition at line 2701 of file waa.c.
References estat::arg, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, and waa__find_common_base().
Referenced by bld__work(), delay__work(), sync__work(), and up__work().
| static int waa__find_common_base | ( | int | argc, | |
| char * | args[], | |||
| char ** | normalized[] | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Wrapper for waa__find_common_base2.
Definition at line 268 of file waa.h.
References waa__find_common_base2().
Referenced by au__work(), cat__work(), ci__work(), cm__detect(), cm__uncopy(), cm__work(), df__work(), ign__work(), info__work(), log__work(), prp__g_work(), prp__l_work(), prp__s_work(), res__work(), rev__work(), st__work(), and waa__find_base().
| int waa__find_common_base2 | ( | int | argc, | |
| char * | args[], | |||
| char *** | normalized, | |||
| int | flags | |||
| ) |
Given a list of path arguments the base path and relative paths are returned.
Given a list of path arguments the base path and relative paths are returned.
This function calculates the common root of the given paths, and tries to find a working copy base there (or above). It returns the paths of the parameters relative to the base found.
Eg.: for /a/wc/sub/sub2 and /a/wc/file it returns
base=/a/wcnormalized[0] =sub/sub2normalized[1] =file
We have to find a wc root before we can load the entries file; so we'd have to process the given paths twice, possibly each time by prepending the current working directory and so on; that's why this function returns a block of relative path pointers. These have just to be walked up to the root to process them (eg. mark for processing).
*normalized should be free()d after use; but as the converted arguments are all allocated one by one it won't help that much.
- Note:
- In case no matching base is found, the common part of the paths is returned as base, and the paths are normalized relative to it.
ENOENTis returned.
- Todo:
- Should that be changed to base="/"?
normalized[0]. argc in the caller will still be 0!
- If we have a dir-file, we look only from the current directory below - so fake a parameter.
- If we have no dir-file:
- If we find a base, we fake a parameter and show only below.
- If we find no base, we believe that we're at the root of the wc.
The parameter must not be shown as "added" ("n...") - because it isn't.
For the case that the WC root is "/", and we shall put a "./" in front of the normalized paths, we need an additional byte per argument, so that eg. "/etc" can be changed to "./etc" - see the PDS comments.
In order to correctly handle cases like "/symlink/to/a/directory/subd/file", we do a realpath() call of the directory of the argument (with ".../" assumed to be ".../."), and use that as base path for the filename.
Definition at line 2287 of file waa.c.
References action, BUG_ON, DEBUGP, FCB__NO_REALPATH, FCB__PUT_DOTSLASH, FILTER__ALL, FSVS_EXP_WC_CONF, FSVS_EXP_WC_ROOT, GWD_CONF, hlp__alloc(), hlp__pathcopy(), hlp__strnalloc(), IF_FREE, actionlist_t::only_opt_filter, OPT__FILTER, opt__load_settings(), opt__set_int(), PATH_SEPARATOR, PRIO_ETC_WC, PRIO_MUSTHAVE, st__status_string_fromint(), start_path, start_path_len, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, waa__get_waa_directory(), waa__open(), wc_path, and wc_path_len.
Referenced by ign__rign(), and waa__find_common_base().
| static int waa__get_gwd_flag | ( | const char *const | extension | ) | [inline, static] |
Function that returns the right flag for the wanted file.
To be used in calls of waa__get_waa_directory().
Definition at line 299 of file waa.h.
References GWD_CONF, and GWD_WAA.
Referenced by delay__work(), hsh___new_bare(), prp__unlink_db_for_estat(), waa__delete_byext(), and waa__open().
| int waa__get_tmp_name | ( | const char * | base_dir, | |
| char ** | output, | |||
| apr_file_t ** | handle, | |||
| apr_pool_t * | pool | |||
| ) |
Returns a distict name and filehandle.
Returns a distict name and filehandle.
If base_dir is NULL, a default path is taken; else the string is copied and gets an arbitrary postfix. If base_dir ends in PATH_SEPARATOR, "fsvs" is inserted before the generated postfix.
*output gets set to the generated filename, and must not be free()d.
Definition at line 2912 of file waa.c.
References BUG_ON, cch__add(), cch__entry_set(), cache_entry_t::data, filename, cache_entry_t::len, PATH_SEPARATOR, and STOPIF.
Referenced by cb__open_tmp(), ci__getmsg(), df___type_def_diff(), rev__get_text_to_tmpfile(), and rev__install_file().
| int waa__get_waa_directory | ( | char * | path, | |
| char ** | erg, | |||
| char ** | eos, | |||
| char ** | start_of_spec, | |||
| int | flags | |||
| ) |
This function determines the directory used in the WAA area for the given path.
This function determines the directory used in the WAA area for the given path.
In erg a pointer to an static buffer (at least as far as the caller should mind!) is returned; eos, if not NULL, is set to the end of the string. start_of_spec points at the first character specific to this file, ie. after the constant part of $FSVS_WAA or $FSVS_CONF and the PATH_SEPARATOR.
flags tell whether the path is in the WAA (GWD_WAA) or in the configuration area (GWD_CONF); furthermore you can specify that directories should be created as needed with GWD_MKDIR.
The intermediate directories are created, so files can be created or read directly after calling this function.
Definition at line 473 of file waa.c.
References BUG, BUG_ON, conf_tmp_fn, conf_tmp_path, cs__md5tohex(), DEBUGP, GWD_CONF, GWD_MKDIR, GWD_WAA, Mbin2hex, OPT__SOFTROOT, PATH_SEPARATOR, STOPIF, waa___get_path_md5(), waa__mkdir(), waa_tmp_fn, waa_tmp_path, WAA_WC_MD5_CHARS, and wc_path.
Referenced by delay__work(), hsh___new_bare(), ign___load_group(), prp__unlink_db_for_estat(), st__print_entry_info(), waa__create_working_copy(), waa__delete_byext(), waa__find_common_base2(), waa__make_info_link(), and waa__open().
| int waa__given_or_current_wd | ( | char * | name, | |
| char ** | erg | |||
| ) |
Returns the given directory or, if NULL , getcwd() .
Returns the given directory or, if NULL , getcwd() .
This function takes the parameter name, and returns a freshly allocated bit of memory with the given value or - if NULL - the current working directory.
That the string is always freshly allocated on the heap makes sense in that callers can always just free it.
Definition at line 808 of file waa.c.
References hlp__strdup(), STOPIF, and waa__save_cwd().
Referenced by url__work(), and waa__open_byext().
| int waa__init | ( | void | ) |
Initialize WAA operations.
Initialize WAA operations.
If not a WAA-less operation, find the WAA and define an ignore pattern.
- Todo:
- remove when gcc doesn't warn about
strlen("const") initializers. See debian bug #60xxxx. And see below for WAA_PATH, too.
Definition at line 159 of file waa.c.
References action, conf_tmp_fn, conf_tmp_path, DEBUGP, DEFAULT_CONF_PATH, DEFAULT_CONFIGDIR_SUB, DEFAULT_WAA_PATH, ext_tmp, hlp__alloc(), hlp__lstat(), hlp__pathcopy(), sstat_t::ino, actionlist_t::is_import_export, actionlist_t::is_readonly, max, OPT__CONF_PATH, OPT__CONFIG_DIR, opt__set_int(), opt__set_string(), OPT__SOFTROOT, opt__variable_from_option(), OPT__WAA_PATH, PRIO_MUSTHAVE, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, waa___init_path(), WAA__MAX_EXT_LENGTH, waa_stat, waa_tmp_fn, waa_tmp_path, waa_tmp_path_len, and WAA_WC_MD5_CHARS.
Referenced by main().
| int waa__input_tree | ( | struct estat * | root, | |
| struct waa__entry_blocks_t ** | blocks, | |||
| action_t * | callback | |||
| ) |
Read the dir file for the current working directory.
Read the dir file for the current working directory.
This may silently return -ENOENT, if the waa__open fails.
The callback is called for every entry read; but for performance reasons the path parameter will be NULL.
Definition at line 1612 of file waa.c.
References approx_entry_count, BUG_ON, estat::by_inode, estat::child_index, waa__entry_blocks_t::count, DEBUGP, estat::entry_count, filename, waa__entry_blocks_t::first, HEADER_LEN, hlp__alloc(), max_path_len, sstat_t::mode, estat::name, waa__entry_blocks_t::next, ops__allocate(), ops__load_1entry(), estat::other_revs, estat::parent, waa__entry_blocks_t::prev, estat::repos_rev, estat::st, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, estat::strings, TREE_DAMAGED, waa__entry_block, waa__header_line, waa__insert_entry_block(), waa__open_dir(), WAA__READ, and WAA_VERSION.
Referenced by cat__work(), cm__uncopy(), cm__work(), log__work(), prp__s_work(), and waa__read_or_build_tree().
| static int waa__insert_entry_block | ( | struct estat * | entry, | |
| int | count | |||
| ) | [inline, static] |
Simple wrapper; inserts entries at the start of the list.
Definition at line 317 of file waa.h.
References waa__entry_block, and waa__new_entry_block().
Referenced by ops__traverse(), and waa__input_tree().

| int waa__load_repos_urls | ( | char * | dir, | |
| int | reserve_space | |||
| ) |
Wrapper for waa__load_repos_urls_silent().
| int waa__load_repos_urls_silent | ( | char * | dir, | |
| int | reserve_space | |||
| ) |
Load the URLs associated with dir (or current working directory, if dir is NULL).
| int waa__make_info_link | ( | char * | directory, | |
| char * | name, | |||
| char * | dest | |||
| ) |
Creates a symlink in the WAA.
Creates a symlink in the WAA.
Normally this is used to mark the base directory used in some WAA path, ie. if you are versioning /etc, you'll get a symlink $WAA/18/2f/153bd94803955c2043e6f2581d5d/_base pointing to /etc .
Definition at line 779 of file waa.c.
References GWD_CONF, GWD_MKDIR, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, and waa__get_waa_directory().
Referenced by waa__create_working_copy().

| int waa__mkdir | ( | char * | dir, | |
| int | including_last | |||
| ) |
Create a directory, ignore EEXIST, and use a default mask.
Create a directory, ignore EEXIST, and use a default mask.
- Note:
- The mask used is
0777- so mind your umask!
Definition at line 334 of file waa.c.
References STOPIF, and waa__mkdir_mask().
Referenced by rev__install_file(), waa__close(), waa__create_working_copy(), waa__get_waa_directory(), waa__mkdir_mask(), and waa__open().

| int waa__mkdir_mask | ( | char * | dir, | |
| int | including_last, | |||
| int | mask | |||
| ) |
Create a directory; ignore EEXIST.
Create a directory; ignore EEXIST.
If it already exists, no error is returned.
If needed, the structure is generated recursively.
With including_last being 0 you can give a filename, and make sure that the directories up to there are created. Because of this we can't use apr_dir_make_recursive() - We'd have to cut the filename away, and this is done here anyway.
Definition at line 354 of file waa.c.
References BUG_ON, DEBUGP, PATH_SEPARATOR, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, and waa__mkdir().
Referenced by rev___undo_change(), and waa__mkdir().

| int waa__new_entry_block | ( | struct estat * | entry, | |
| int | count, | |||
| struct waa__entry_blocks_t * | previous | |||
| ) |
Insert an entry block with count entries into the waa__entry_blocks list, to get it updated later by waa__update_tree().
The list of entries to be updated is registered after the given block.
Definition at line 2673 of file waa.c.
References waa__entry_blocks_t::count, waa__entry_blocks_t::first, hlp__alloc(), waa__entry_blocks_t::next, waa__entry_blocks_t::prev, and STOPIF.
Referenced by waa__insert_entry_block().

| int waa__open | ( | char * | path, | |
| const char * | extension, | |||
| int | flags, | |||
| int * | filehandle | |||
| ) |
Base function to open files in the WAA.
For the flags the values of creat or open are used; the mode is 0777, so take care of your umask.
If the flags include one or more of O_WRONLY, O_TRUNC or O_RDWR the file is opened as a temporary file and must be closed with waa__close(); depending on the success value given there it is renamed to the destination name or deleted.
This temporary path is stored in a per-filehandle array, so there's no limit here on the number of written-to files.
If the flags include O_APPEND, no temporary file is used, and no filehandle is stored - do simply a close().
For read-only files simply do a close() on their filehandles.
Does return ENOENT without telling the user.
- Note:
- If extension is given as
NULL, only the existence of the given WAA directory is checked. So the caller gets a0or an error code (likeENOENT); flags and filehandle are ignored.
Definition at line 586 of file waa.c.
References action, BUG_ON, DEBUGP, waa___temp_names_t::dest_name, ext_tmp, hlp__lstat(), hlp__realloc(), hlp__strdup(), actionlist_t::is_readonly, PATH_SEPARATOR, STOPIF, target_name_array_len, waa___temp_names_t::temp_name, waa__get_gwd_flag(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__mkdir().
Referenced by waa__find_common_base2(), and waa__open_byext().
| int waa__open_byext | ( | char * | entry_name, | |
| char * | extension, | |||
| int | mode, | |||
| int * | fh | |||
| ) |
Wrapper function for waa__open().
Wrapper function for waa__open().
The entry_name may be NULL; then the current working directory is taken. write is open mode, like used for open(2) (O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC) and is given to waa__open().
ENOENT is returned without giving an error message.
Definition at line 903 of file waa.c.
References IF_FREE, STOPIF, waa__given_or_current_wd(), and waa__open().
Referenced by cs___update_manber(), cs__read_manber_hashes(), ign__load_list(), ign__save_ignorelist(), res__mark_conflict(), res__remove_aux_files(), url__load_list(), url__output_list(), and waa__open_dir().
| int waa__open_dir | ( | char * | wc_base, | |
| int | write, | |||
| int * | fh | |||
| ) |
Wrapper function.
Opens a dir-file for the directory in the WAA.
- Todo:
- Should possibly be eliminated.
Definition at line 928 of file waa.c.
References WAA__DIR_EXT, and waa__open_byext().
Referenced by waa__input_tree(), and waa__output_tree().
| int waa__output_tree | ( | struct estat * | root | ) |
Write the dir file for this root .
Write the dir file for this root .
Here the complete entry tree gets written to a file, which is used on the next invocations to determine the entries' statii. It contains the names, sizes, MD5s, devices, inode numbers, parent, mode and time informations, and a reference to the parent to re-build the tree.
- Todo:
- Currently hardlinks with duplicate inode-numbers are not well done in fsvs.
Format
This file has a single header line with a defined length; it is padded before the newline with spaces, and the last character before the newline is a $ . The other lines have space-delimited fields, and a \0 delimited name at the end, followed by a newline.
Order of entries in the file
We always write parents before childs, and (mostly) lower inode numbers before higher; mixing the subdirectories is allowed. This allows us to rebuild the tree in one pass (because the parents are already known), and gives us nearly linear reading on the storage media (because the inodes are mostly in harddisk order, there's not much back-seeking necessary).
As a consequence the root entry . is always the first one in the written file.
- Note:
- If we were going strictly in inode-order, we would have to jump over some entries (if the parent directory has a higher inode number than this entry and the [hard disk] head is already further down), and then have a second run through ... (or possibly a third, and so on). That's more complexity than wanted, and doesn't bring performance. So currently only one run; hard disk must move back sometimes.
directory Array
We use one array, named directory , to store pointers in the estat::by_inode arrays we're traversing (which are defined to be NULL-terminated).
We just have to find the next inode in the active directories; they are already sorted by inode, so that's very easy.
Here's a small drawing in ASCII, followed by a graphviz version.
* (struct estat) * ^ * | * xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxN xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxN xxN xxxxN * ^ ^ ^ ^ * /->d >-/ | | | * | d >----------------------------/ | | * | d >------------------------------------/ | * | d >------------------------------------------------/ * | * directory *
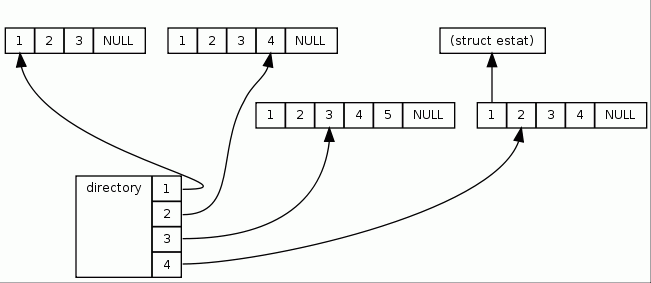
The d's show the directories-array with 4 entries.
We don't really store the parent inode numbers in the file; that wouldn't be enough, anyway - as soon as there are two or more filesystems, they would collide.
So instead of the inode number we store the number of the entry *in the file*; so the root inode (which is always first) has parent_ino=0 (none), its children get 1, and so on. That means that as long as we allocate the memory block in a single continuous block, we don't have to search any more; we can just reconstruct the pointers to the parent. We keep the directory-array sorted; so we have to insert a new directory at the correct position, but can otherwise output very fast. So for the array [10 20 30 40 50 60 70] the element 10 is written; the next one, say 35, is inserted at the correct position: [20 30 35 40 50 60 70] Again the first (smallest) element is written, and so on.
Definition at line 1211 of file waa.c.
References BUG_ON, estat::by_inode, DEBUGP, dir___f_sort_by_inode(), dir__sortbyinode(), estat::entry_count, estat::file_index, HEADER_LEN, hlp__calloc(), hlp__realloc(), IF_FREE, sstat_t::ino, max_path_len, estat::name, ops__calc_path_len(), ops__has_children(), ops__save_1entry(), ops__should_entry_be_written_in_list(), estat::parent, estat::path_len, estat::st, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, estat::to_be_sorted, estat::url, waa___find_position(), waa__close(), waa__header_line, waa__open_dir(), WAA__WRITE, and WAA_VERSION.
Referenced by au__work(), bld__work(), ci__work(), cm__uncopy(), cm__work(), co__work(), prp__s_work(), res__work(), rev__work(), sync__work(), and up__work().
| int waa__partial_update | ( | struct estat * | root, | |
| int | argc, | |||
| char * | normalized[], | |||
| char * | orig[], | |||
| struct waa__entry_blocks_t * | blocks | |||
| ) |
The given paths are looked for in the entries tree, are marked for update, and their parents are flagged.
The given paths are looked for in the entries tree, are marked for update, and their parents are flagged.
We get a tree starting with root, and all entries from normalized get estat::do_userselected and estat::do_this_entry set. These flag gets used by waa__update_tree().
Definition at line 2595 of file waa.c.
References estat::arg, BUG_ON, DEBUGP, estat::do_child_wanted, estat::do_this_entry, estat::do_userselected, estat::flags, hlp__lstat(), OPS__CREATE, OPS__FAIL_NOT_LIST, OPS__ON_UPD_LIST, ops__traverse(), ops__update_single_entry(), OPT__PATH, estat::parent, PATH_PARMRELATIVE, RF_ADD, RF_ISNEW, estat::st, STOPIF, STOPIF_CODE_ERR, and waa__update_tree().
Referenced by waa__read_or_build_tree().
| int waa__read_or_build_tree | ( | struct estat * | root, | |
| int | argc, | |||
| char * | normalized[], | |||
| char * | orig[], | |||
| action_t * | callback, | |||
| int | return_ENOENT | |||
| ) |
Reads the entry tree or, if none stored, builds one.
Reads the entry tree or, if none stored, builds one.
argc and normalized tell which entries should be updated.
We return the -ENOENT from waa__input_tree() if no working copy could be found. ENOENT is returned for a non-existing entry given on the command line.
The callback is called for every entry read by waa__input_tree(), not filtered like the normal actions.
Definition at line 2199 of file waa.c.
References action, DEBUGP, hlp__match_path_envs(), actionlist_t::local_uninit, OPT__PATH, PATH_CACHEDENVIRON, STOPIF, waa__input_tree(), and waa__partial_update().
Referenced by au__work(), ci__work(), cm__detect(), df__work(), ign__work(), info__work(), res__work(), rev__work(), st__work(), and up__work().

| int waa__save_cwd | ( | char ** | where, | |
| int * | ret_len, | |||
| int | additional | |||
| ) |
Store the current working directory.
Store the current working directory.
This is more or less a portable reimplementation of GNU getcwd(NULL,0) ... self-allocating the needed buffer.
where gets the cwd, and must be free()d; the optional ret_len can be set to the actual length of the cwd.
If the caller wants to append some path to the end, and knows how many bytes are needed, the additional bytes can be requested.
If the cwd has been removed, we get ENOENT. But returning that would not necessarily signal a fatal error to all callers, so we return ENOTDIR in that case.
Definition at line 294 of file waa.c.
References hlp__realloc(), STOPIF, and STOPIF_CODE_ERR.
Referenced by co__work(), main(), waa___get_path_md5(), and waa__given_or_current_wd().
| int waa__set_working_copy | ( | const char const * | wc_dir | ) |
Stores the path of the working copy.
Not needed if waa__find_common_base or similar is called.
Stores the path of the working copy.
The dir must be absolute; this function makes an own copy, so the value will be unchanged.
Definition at line 2987 of file waa.c.
References BUG_ON, hlp__strnalloc(), PATH_SEPARATOR, STOPIF, wc_path, and wc_path_len.
Referenced by url__work(), and waa__create_working_copy().


| int waa__update_tree | ( | struct estat * | root, | |
| struct waa__entry_blocks_t * | cur_block | |||
| ) |
This function traverses the tree and sets entry_status for the marked entries.
This function traverses the tree and sets entry_status for the marked entries.
On input we expect a tree of nodes starting with root; the entries that need updating have estat::do_userselected set, and their children get marked via ops__set_todo_bits().
On output we have estat::entry_status set; and the current action->local_callback gets called.
It's not as trivial to scan the inodes in ascending order as it was when this part of code was included in waa__input_tree(); but we get a list of (location, number) blocks to run through, so it's the same performance-wise.
This function consumes the list of entry blocks, ie. it destroys their data - the first pointer gets incremented, count decremented.
Threading
We could use several threads, to get more that one lstat() to run at once. I have done this and a patch available, but testing on linux/x86 on ext3 seems to readahead the inodes, so the wall time got no shorter.
If somebody wants to test with threads, I'll post the patch.
For threading there has to be some synchronization - an entry can be done only if its parent has been finished. That makes sense insofar, as when some directory got deleted we don't need to lstat() the children - they must be gone, too.
KThreads
On LKML there was a discussion about making a list of syscalls, for getting them done without user/kernel switches. (About 2007 or so? Don't even know whether that was merged in the end.)
On cold caches this won't really help, I think; but I didn't test whether that would help for the hot-cache case.
Design
- If the parent of the current entry is removed, this entry is too; skip the other checks.
- Check current status.
-
All entries that are not a directory now can be printed immediately; decrement parent's
unfinishedcounter. -
Directory entries
-
These increment their parent's
unfinishedvalue, as they might have children to do. -
If they have no known entries (have been empty) they may get checked for changes (
waa__update_dir()), and are finished - decrement parent'sunfinishedcounter. -
Else they wait for their
child_indexvalue to reach theentry_countnumber; then, as soon as theirunfinishedvalue gets zero, they're really done.
-
These increment their parent's
-
If a directory has no more
unfinishedentries, it can be checked for changes, and is finished - decrement parent'sunfinishedcounter.
The big obstacle is that arbitrary (sub-)paths might be wanted by the user; so we have to take great care about the child-counting.
Definition at line 2022 of file waa.c.
References ac__dispatch, action, estat::by_inode, estat::by_name, estat::child_index, waa__entry_blocks_t::count, DEBUGP, estat::do_child_wanted, estat::do_filter_allows, estat::do_filter_allows_done, estat::do_this_entry, estat::do_userselected, estat::entry_count, estat::entry_status, waa__entry_blocks_t::first, FS_CHANGED, FS_LIKELY, FS_REMOVED, FS_REPLACED, actionlist_t::keep_children, estat::local_mode_packed, sstat_t::mode, estat::name, waa__entry_blocks_t::next, estat::old_rev_mode_packed, ops__mark_parent_cc, ops__update_filter_set_bits(), PACKED_to_MODE_T, estat::parent, estat::st, STOPIF, estat::strings, TEST_PACKED, estat::unfinished, and waa___finish_directory().
Referenced by waa__partial_update().
Variable Documentation
| char * conf_tmp_fn |
Definition at line 63 of file waa.c.
Referenced by main(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__init().
| char * conf_tmp_path |
Definition at line 63 of file waa.c.
Referenced by main(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__init().
First block for to-be-updated pointers.
Definition at line 99 of file waa.c.
Referenced by waa__input_tree(), and waa__insert_entry_block().
| char * waa_tmp_fn |
Definition at line 63 of file waa.c.
Referenced by hsh___new_bare(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__init().
| char* waa_tmp_path |
Buffers for temporary filename storage.
Buffers for temporary filename storage.
They are long enough to hold the waa path plus the 3-level deep subdirectory structure for cache and data files. The conf path plus additional data gets it own buffers.
Definition at line 63 of file waa.c.
Referenced by hsh___new_bare(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__init().
| int waa_tmp_path_len |
Length of paths of temporary files.
Definition at line 96 of file waa.c.
Referenced by ign___load_group(), and waa__init().
| char* wc_path |
Our current WC base.
Our current WC base.
Valid after a successfull call to waa__find_common_base().
Definition at line 104 of file waa.c.
Referenced by cm___dump_list(), cm___get_base_source(), cm___make_copy(), cm___not_below_wcpath(), cm__detect(), delay__work(), hlp__format_path(), hlp__match_path_envs(), ign___load_group(), ign__compile_pattern(), ign__save_ignorelist(), sync__work(), url__load_nonempty_list(), waa__create_working_copy(), waa__find_common_base2(), waa__get_waa_directory(), and waa__set_working_copy().
| int wc_path_len |
How much bytes the wc_path has.
Definition at line 106 of file waa.c.
Referenced by cm___not_below_wcpath(), hlp__format_path(), hlp__match_path_envs(), ign__compile_pattern(), ign__work(), waa__find_common_base2(), and waa__set_working_copy().
 1.5.9
1.5.9